- +86-13775339109
- Jessica@nq-fiberglass.cn
- No 61 Fangxian, Danyang, Jiangsu
Carbon fiber fabric, also known as carbon fiber cloth, is prized for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, heat resistance, and durability—making it a go-to material in industries like aerospace, automotive, sports, and construction.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to choose the right type of carbon fiber, understand the key factors that affect its price, and explore why it’s preferred across so many demanding applications. Whether you’re new to composites or refining your craft, this guide helps you get it right from the start.
Table of Contents
ToggleCarbon fiber fabric is produced by weaving groups of carbon filaments—known as tows—into cloth with specific patterns, such as plain, twill, or satin. The “K” rating – 3K, 12K, etc.– refers to the number of filaments in each bundle. This construction provides the fabric with robust bi-directional strength and makes it visually striking. Compared to other textile materials, woven carbon fiber boasts a superior strength-to-weight ratio with tensile strengths up to 700 ksi and a density of approximately 1.75 g/cm³. The table below shows how it stacks up against common textiles:
Material | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Density (g/cm³) | Flexibility | Fatigue Resistance |
Carbon Fiber | up to 4820 | 1.75 | Moderate | Excellent |
Glass Fiber | up to 3500 | 2.6 | High | Good |
Kevlar | up to 3620 | 1.44 | High | Excellent |
Cotton | up to 400 | 1.54 | Very High | Poor |
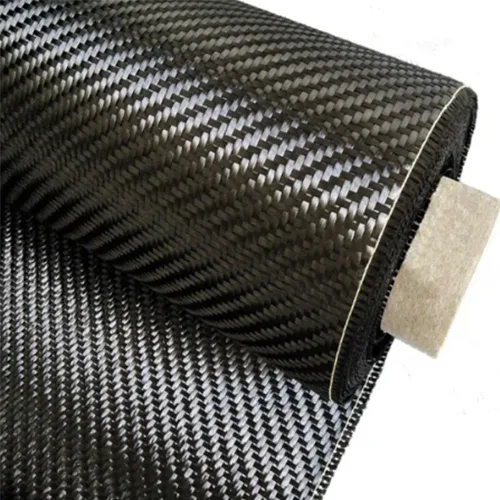

Plain weave uses a simple over-under pattern that offers excellent stability and resists fraying. This structure makes it ideal for flat surfaces or panels, where dimensional control is important. Its tightly woven design not only adds strength but also helps prevent the fabric from shifting during handling or layup. The tighter the weave, the stiffer the fabric—offering excellent strength but less flexibility for wrapping around curves.
Common applications include:
Aerospace components
Medical devices
Marine parts
Twill weave is distinctive for its diagonal ribs. This structure allows the fabric to drape more easily, making it ideal for shaping curved or complex surfaces. Its improved drapability also makes twill weave easier to work with.
Common applications include:
Phone cases
Car parts
Bike frames
Automotive panels

Carbon Fiber Biaxial Fabric is a non-woven material where carbon fibers are stitched in two directions—typically ±45° or 0°/90°—to enhance strength and stability. Unlike woven fabric, it offers better drapability and load distribution, making it ideal for demanding applications. Biaxial carbon fabric is widely used in structural reinforcement, laminates, and composite layups where directional strength is essential.
Common applications include:
Marine structures
Automotive parts
Wind energy components
Aerospace applications

Unidirectional fabrics all fibers in a single direction. This design makes them ideal for applications where loads are applied mainly in one direction, such as beams or spars. They provide high stiffness to the final part, which is essential in industries demanding focused strength.
Common applications include:
Aerospace structural components
Wind energy turbine blades
Sporting equipment beams
Automotive chassis reinforcement

Pre-impregnated carbon fiber (prepreg) is made by saturating fibers with resin beforehand. This ensures consistent tension and reduces errors during layup. Prepregs are flexible and enable faster lamination, making them essential for high-performance applications.
Common applications include:
Aerospace components
Racing parts
Medical devices
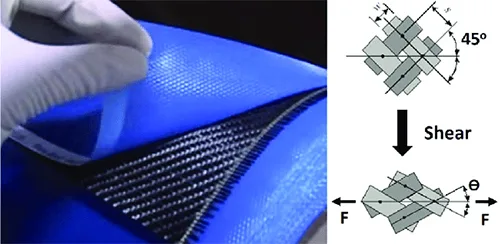
There are a number of elements that influence carbon fiber fabric pricing, from thickness and weight, to process and purity. Even the weave type, layup and production process all contribute. For anyone dealing in composites, understanding this information is crucial to navigating the mix of performance, price and end application requirements.
When working with carbon fiber fabric, the more layers you use to build thickness, the more material and resin are required—leading to higher overall costs. Factors such as fabric type, weave pattern, fiber grade, and number of plies directly affect the price of carbon fiber cloth. For example, thicker laminates demand careful layup to avoid wrinkles, gaps, or resin buildup, as these issues can reduce strength and increase waste.
The price of carbon fiber fabric largely depends on its weight (K rating). 3K fabrics are lightweight, flexible, and easy to mold around complex curves, but they require more layers, which increases total material and labor costs. In contrast, 12K fabrics are heavier and cover more area with fewer layers, making them more affordable, though less flexible. Choosing the right weave direction—such as ±45° or 0°/90°—also affects performance and cost efficiency.

When performing carbon fiber fabric layup, you need to layer multiple sheets of carbon fiber cloth at specific angles—such as 0°, 45°, and 90°—to achieve optimal strength and stiffness in different directions. These layers are then impregnated with resin and cured under vacuum pressure. The type of fabric you choose not only affects the final part’s performance but also plays a key role in the overall manufacturing cost.
Layup Angle | Grammage (gsm) | Weave Structure | Estimated Price (USD/㎡) | Width (mm) | Thickness (mm) |
0° | 200–240 | Unidirectional (UD) | $20–$28 | 1000–1200 | 0.15–0.25 |
45° | 200–300 | ±45° Biaxial (NCF or Woven) | $24–$32 | 1000–1500 | 0.20–0.30 |
90° | 200–240 | Unidirectional (UD) | $20–$28 | 1000–1200 | 0.15–0.25 |
0°/90° | 300–600 | Plain / Twill Weave | $28–$40 | 1000–1500 | 0.20–0.35 |
±45° | 400–800 | Biaxial Non-Crimp Fabric (NCF) | $35–$50 | 1200–1600 | 0.30–0.50 |
Weaving style strongly affects the price of carbon fiber fabric, as well as its suitability for different applications.
Plain and Twill Weave Carbon Fiber Fabric Plain weave offers a tight, stable pattern that requires precise manufacturing to avoid defects, making it ideal for structural parts needing strength and stability. Twill weave is softer and better for curved surfaces, often used in automotive and aerospace components for its flexibility and aesthetic appeal. However, twill’s complex production and higher waste usually mean a higher cost.
Carbon Fiber Kevlar Fabric Blending carbon fiber with Kevlar produces a tough, impact-resistant fabric perfect for protective gear, military, and high-performance sports applications. Weaving these fibers together, especially with colors like black or blue carbon fiber fabric, involves specialized equipment and extra processing steps, increasing the price.
Carbon fiber fabric supply depends on advanced materials and technology, mainly from China, Japan, and the US. Demand is rising fast in aerospace, automotive, renewable energy, and sports due to lightweight and eco trends. Supply often lags demand, causing price changes, But new technologies and recycling have improved price stability.
From the very first moments of carbon fiber’s existence, fabric and its composites have been in many fields, changing the entire world’s construction and application. Its strength, low weight and long life have made it a go-to for industries that require durable lightweight components. Carbon fiber fabric cloth products are everywhere — planes, cars, sports equipment, even in our everyday accessories.
The aerospace industry uses woven carbon fiber to reduce weight and boost fuel efficiency. With fibers at 0° and 90°, it offers multi-directional strength ideal for wings, fuselages, and interiors. Unlike unidirectional types, woven fabric suits curved, complex shapes. Carbon fiber parts are made by laying the cloth and adding resin, creating lightweight, durable composites that resist rust and last for years.

Car makers use carbon fiber to build lighter, more fuel-efficient vehicles. It appears in hoods, roofs, wheels, and motorcycle armor for its strength and low weight. Woven carbon fiber suits curved parts better than linear strands, offering both durability and sleek design. Unlike steel or aluminum, it resists rust and keeps its shine, even in everyday trim and covers.

Sports gear uses woven carbon fiber to boost strength, reduce weight, and improve comfort. Bikes, rackets, and clubs benefit from its flexibility and durability. Resin-infused layups create gear that resists breaking and lasts longer. For pros and hobbyists alike, carbon fiber cuts fatigue and enhances performance on road, court, or water.
Carbon fiber jewelry is beginning to establish itself as a fresh, powerful alternative to gold or silver. Its brilliance and hardness ensure it will appear stunning for decades. Daily accessories — phone cases, wallets, watches — often feature carbon fiber for its aesthetic and light weight.New areas such as robotics and sustainable energy are pushing carbon fiber in innovative directions — leveraging its special properties to build lighter, stronger technology.
Carbon fiber fabric is unique for its combination of durability, weight and aesthetics. This is what makes it such a clever choice for applications around the globe, from couture to construction.
Carbon fiber’s high strength-to-weight ratio—five times stronger than steel and twice as stiff—makes it ideal for airplanes, cars, and sports gear. Lightweight yet durable, it’s also popular in belts and jewelry. For motorcycle gear and professionals who value every gram, carbon fiber offers superior protection and lasting durability without the weight.
Carbon fiber fabric is prized for its durability—it resists rust, corrosion, and harsh chemicals, making it ideal for long-lasting outdoor gear and jewelry. Unlike silver or gold, it won’t tarnish and keeps its shine with little upkeep. Its toughness also makes it perfect for protective gear like motorcycle suits and helmets.

Carbon fiber cloth offers great versatility for artisans—it can be molded, woven, or laminated to fit any need. Woven cloth is preferred over unidirectional for flexible shapes like car panels, phone cases, and furniture, where fit and appearance matter. Varying weaves and thicknesses give designers endless custom options, making carbon fiber ideal for unique, tailored projects.
The global’s top carbon fiber manufacturers influence the manufacturing and utilization of carbon fiber fabric and carbon fiber cloth. With centers of excellence in Germany, Japan, and the US and an extensive presence in Europe, North America, and Asia. Most of these companies have worked in this area for decades, some as far back as 1863, 1926 or 1948. Their roots run deep — and so does their expertise. With workforces that can number up to nearly 4,700 at more than 30 sites around the world, these companies are huge — and global.
Here’s a more detailed look at some of these key players:
Toray Industries is a global leader in high-performance materials like carbon fiber, synthetic fibers, and chemicals. Known for strong R&D and innovation, it serves aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical industries with reliable quality and a solid supply chain.
Teijin Limited is a Japan-based global company specializing in high-performance fibers like carbon and aramid, plastics, electronics, healthcare, and energy solutions. Known for strong R&D, it leads in carbon fiber composites used in aerospace, automotive, and sports. The company focuses on sustainability and innovation, recognized as an industry technology leader.
Danyang NQ Glass Fiber Weaving Co., Ltd.:
Danyang NQ Glass Fiber Weaving Co., Ltd., founded in 2007 in Jiangsu, China, specializes in alkali-resistant fiberglass mesh, reinforcement mesh, self-adhesive tape, and screening mesh. With a 7 million sqm annual capacity, ISO9001 certification, and strict quality control, it serves construction and industrial markets worldwide, earning a strong reputation for quality and customer service.
A technology company that provides solutions for materials, chemicals, and carbon fiber cloth to bring technological advancements and address key industrial, social, and environmental challenges faced by many fields such as aviation, automotive, electronics, healthcare, water treatment, and air management.
SGL Carbon, based in Germany, is a global leader in carbon materials, including carbon fibers, composites, and graphite products. Serving automotive, aerospace, energy, and industrial sectors, it offers high-performance, heat- and corrosion-resistant solutions. Known for innovation and sustainability, SGL holds top positions in carbon fiber composites and graphite electrodes.
Hexcel Corporation is a leading U.S.-based composite materials manufacturer specializing in carbon fiber, prepregs, and resins. Their products serve aerospace, defense, and industrial markets. Hexcel supplies key materials to Boeing, Airbus, and others, with global manufacturing sites and strong R&D capabilities. The company drives technological innovation and sustainability, making it a major supplier in the industry.
Hyosung Corporation is a South Korean global conglomerate founded in 1966, specializing in textiles, chemicals, heavy industry, energy, and IT. Known for sustainable brands like CREORA®, it excels in energy systems and polymer production. With operations in over 60 countries, Hyosung focuses on innovation and strong ESG practices to drive sustainable growth and global leadership.
Zoltek Companies, Inc., part of Toray Industries, is a global leader in industrial carbon fiber production. It offers cost-effective Panex® fiber, flame-resistant Pyron®, and recycled carbon fiber. With plants in the US, Hungary, and Mexico, Zoltek serves wind energy, automotive, and marine industries. Its strengths include high production capacity, competitive pricing, and versatile applications.
Formosa Plastics is a major Taiwanese company specializing in petrochemicals, plastics, and synthetic resins. It produces PVC, polyethylene, and other polymers for industries like construction, packaging, and electronics. Known for large-scale, efficient production and strong R&D, Formosa Plastics emphasizes sustainability and global market presence, making it a key player in the chemical sector.
Nippon Graphite Fiber Co., Ltd.
Nippon Graphite Fiber Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of Mitsubishi Chemical, specializes in high-performance carbon fiber for aerospace, defense, and industrial applications. Its flagship product, DIALEAD®, offers ultra-high modulus and strength. The company is known for precision manufacturing, advanced R&D, and reliable quality, making it a trusted supplier in demanding global markets.
These are essential for anyone handling carbon fiber fabric! They trend quality, supply and new applications. Their worldwide footprint translates into cutting-edge technology, expanded options and reliable availability—wherever you’re located.
Carbon fiber fabric is lightweight, strong, and widely used in cars, planes, sports gear, and even medical tools. Prices vary by weave, grade, and brand. Top manufacturers lead with quality and innovation. Whether you’re a pro or hobbyist, use the right tools and techniques to get the best results. Want to start a project? Compare specs, choose wisely, and share your tips below!
If you have questions or want to discuss your project, feel free to contact us via WhatsApp +86-13775339109, WeChat 13775339100, or email fiberglassmesh@hotmail.com. We’re here to assist you!
Connect with an NQ expert to discuss your product needs and get started on your project.
Carbon fibre is a high-end material that typically has a higher initial cost compared to traditional reinforcement methods, such as steel. The application process is also intricate, requiring skilled technicians and high-quality adhesives, all of which contribute to higher initial expenses.
However, some factors do influence its durability, like its matrix. Furthermore, the intense use of composites and environmental factors could affect its durability and potential applications. In general, scientists anticipate carbon fiber parts to last for over 50 years.
While carbon fiber is a high-performance material with a great strength-to-weight ratio, several alternatives can be considered “better” depending on specific application needs. Graphene, carbon nanotubes, and Kevlar are often cited as potential superior materials. Additionally, Galvorn, a carbon nanomaterial, offers a sustainable and high-performance alternative.
In conclusion, carbon fiber is a unique material with properties that make it an ideal choice for various applications. The characteristic of strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness, and resistance to heat makes a popular choice in industries such as aerospace, automotive, sports, and medical sectors.
If you need a material that is weather-resistant and waterproof, carbon fiber might be a top choice. Carbon fiber is waterproof and resistant to weather when treated to be so. It is suitable for products that need to be mould resistant and easy to clean and disinfect.
While the UV light does not destroy the carbon fibers themselves, it can cause the premature degradation of sheets and panels by degrading their epoxy resin. In this respect, not all carbon fiber products are UV stable.
You can use a bandsaw, scrollsaw, jigsaw, or table saw with a fine-tooth carbide blade. You can also use a CNC router with a carbide bit. For smaller work, a Dremel tool can be used. Once cut, edges can be finished with light sandpaper or a file.
Carbon fibers are available in the range of 800 to 900 Rs. Per kilogram. PTFE coated fabric is available in a wide range of sizes, models, and designs. It is carved by keeping in mind the usability in various industries.
Because carbon fibre is relatively new to the market, research is ongoing to cut the costs of its production – unlike many metals and plastics, which utilise a production refined over decades and even centuries. The manufacturing process is lengthy and complex, requiring skilled engineers to complete.
The aerospace industry has an estimated scrap rate of 30 percent. Over 24,000 tons of carbon fiber waste ends up in landfills or is incinerated every year, despite being worth as much as $630 million.
Carbon fiber fabric is known for being really tough stuff—it’s what Kevlar is made out of. You would be surprised how easy it actually is to sew with. You want the strongest thread you can find for this material. A heavy duty (about 30 wt) poly should do the trick.
Carbon fiber, while strong and lightweight, has several notable disadvantages. These include high cost, susceptibility to impact damage, and difficulty in recycling. Additionally, it can be brittle, making it prone to cracking or fracturing under stress, and repairing damaged components is often complex and expensive.
From the basic properties of carbon fiber, carbon fiber will not deteriorate over time due to its stable chemical structure. However, the carbon fiber surface sizing agent is a polymer that is affected by temperature, humidity and time , so no carbon fiber manufacturer can extend the warranty period beyond two years .