- +86-13775339109
- Jessica@nq-fiberglass.cn
- No 61 Fangxian, Danyang, Jiangsu
Table of Contents
ToggleIf you work in construction, automotive, marine, or industrial manufacturing, chances are you’ve already come across fiberglass. It’s light, strong, and versatile — making it a go-to material in everything from boat hulls to insulation panels. But do you really know what fiberglass is made of, how it’s produced, and why fiberglass cloth is such a valuable product for your projects?
In this guide, you’ll learn everything about fiberglass — from its composition and properties to its wide-ranging applications. By the end, you’ll understand not only what fiberglass is but also how you can use fiberglass cloth to save costs and improve performance.
Fiberglass is a fiber-reinforced plastic where the reinforcing material comes from extremely fine fibers of glass. It combines the durability of glass with the flexibility and lightweight benefits of modern composite materials. This is why you will see fiberglass in such a wide array of applications, including:
Construction: Roofing panels, wall reinforcements, insulation boards, and flooring materials.
Transportation: Automotive body panels, aircraft parts, and boat hulls.
Energy: Wind turbine blades, solar panel reinforcement, and industrial tanks.
Everyday Products: Sports equipment like surfboards, bicycle frames, pools, and hot tubs.
In simple terms, fiberglass provides strength without the heavy weight, offering a cost-effective alternative to materials like steel and carbon fiber. If your goal is to achieve both durability and lightweight performance, fiberglass is one of the best materials available.

The core components of fiberglass are natural raw materials that are widely available:
Silica sand – the primary source of silicon dioxide, giving glass its essential structure.
Soda ash – lowers the melting temperature of the glass mixture.
Limestone – adds stability and durability to the final material.
These ingredients are melted at extremely high temperatures to create molten glass. The molten material is then extruded through microscopic nozzles to produce ultra-thin glass filaments. When woven into fiberglass cloth or mats and combined with resins like polyester or epoxy, these filaments form a composite material that is:
Strong, with high tensile strength capable of handling significant loads.
Resistant to heat, corrosion, and moisture, ensuring longevity in challenging environments.
Affordable and widely available, making it suitable for both large-scale industrial and small-scale consumer projects.
Fiberglass cloth, in particular, is ideal for reinforcing repairs or manufacturing durable components because it allows you to achieve precise shapes and layering without compromising strength.

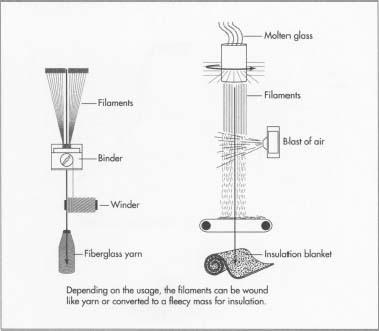
The manufacturing process of fiberglass is as fascinating as it is technical:
The raw materials are melted at temperatures exceeding 1,400°C (2,550°F) to form molten glass.
The molten glass is pulled through tiny nozzles to create continuous fibers that are only a few microns thick.
These fibers are then spun, woven, or chopped into mats, cloths, or tapes.
The material can be combined with resins and molded into virtually any shape, from flat panels to complex curved components.
A remarkable fact about fiberglass production is that one small glass marble can be stretched into nearly 95 miles of fiberglass filament, highlighting its incredible strength-to-weight ratio.
。
Fiberglass comes in multiple grades and forms, depending on the performance requirements of your application. Some of the most common grades include:
Grade | Best For | Key Benefits |
E-glass (Electrical) | Circuit boards, fiber optics | Non-conductive, heat resistant |
S-glass (Structural) | Aerospace, automotive | Extremely high strength-to-weight ratio |
C-glass (Chemical) | Tanks, pipelines | Resistant to corrosion and chemicals |
General Purpose | Insulation, consumer goods | Cost-effective and versatile |
For most construction, repair, and industrial applications, fiberglass cloth or mats are the preferred choice. They are easy to cut, layer, and mold, which makes them ideal for projects such as boat repairs, automotive panels, roofing, and pipeline reinforcements.
Fiberglass offers several key properties that make it indispensable for industrial and consumer applications:
Fiberglass provides a level of strength comparable to metals like steel, but it is far lighter. This makes it particularly valuable in automotive, aerospace, and marine applications, where reducing weight can enhance performance and efficiency.
You do not have to worry about moisture, corrosion, or UV exposure when using fiberglass. Its resistance to environmental factors ensures long-lasting performance, whether you are building outdoor structures or marine vessels.
Fiberglass naturally traps heat, making it an excellent insulator for buildings, industrial systems, and even energy storage units. Its insulating properties can help you improve energy efficiency and reduce heating or cooling costs.
Fiberglass cloth is highly adaptable. You can cut, layer, and mold it into almost any shape, whether you need a flat panel, a curved structural part, or a complex reinforcement design. This flexibility saves you time and materials during fabrication or repair projects.
Fiberglass cloth is used across numerous industries due to its durability, versatility, and affordability:

Feature | Fiberglass | Carbon Fiber |
Strength-to-Weight | High | Higher |
Cost | Affordable | Expensive |
Durability | Resistant to corrosion, heat, and chemicals | Excellent but brittle in impact |
Applications | Construction, automotive, boats, insulation | Aerospace, racing cars, high-performance gear |
While carbon fiber offers exceptional strength and stiffness, it comes with a significantly higher cost and more brittle behavior during impact. For cost-effective, versatile, and widely available reinforcement, fiberglass cloth is usually the better choice, especially for everyday industrial and construction projects.
If you are sourcing fiberglass for your next project, here are the reasons why our fiberglass cloth stands out:
Fiberglass is more than a material — it’s a modern industry essential. Strong, durable, flexible, and cost-effective, it’s perfect for construction, automotive, marine, and energy applications. For repairs or manufacturing, fiberglass cloth is easy to use, affordable, and highly reliable.
Looking for high-quality fiberglass cloth for your projects? Contact us today to get expert recommendations, free samples, and the best pricing for your industry needs.
Connect with an NQ expert to discuss your product needs and get started on your project.
Fiberglass cloth offers an excellent balance of strength, lightweight performance, and affordability. Compared to metals or carbon fiber, it is easier to handle, cost-effective, and resistant to corrosion, heat, and chemicals, making it ideal for construction, automotive, marine, and industrial applications.
Yes, fiberglass cloth is widely used for DIY projects and repairs. You can reinforce boat hulls, car panels, or household structures by layering the cloth with resin. Its flexibility and ease of handling make it suitable for both small-scale repairs and larger projects.
When properly applied and maintained, fiberglass can last for decades. Its durability comes from its resistance to moisture, corrosion, UV exposure, and temperature changes, ensuring long-term performance for both industrial and consumer applications.
Fiberglass cloth comes in various types, each suited for specific applications:
E-Glass (Electrical Grade): Non-conductive and heat-resistant, ideal for electrical applications.
S-Glass (Structural Grade): Offers high strength-to-weight ratio, used in aerospace and automotive industries.
C-Glass (Chemical Grade): Resistant to corrosion, suitable for chemical processing equipment.
General Purpose: Versatile and cost-effective, used in construction and consumer goods.
Fiberglass cloth is known for:
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Provides strength comparable to metals but is much lighter.
Corrosion Resistance: Withstands exposure to moisture, chemicals, and UV rays.
Thermal Insulation: Effective in thermal management applications.
Design Flexibility: Can be molded into various shapes, making it suitable for complex designs.
Fiberglass cloth is widely used in:
Marine Industry: Reinforcing boat hulls and decks.
Automotive Industry: Manufacturing body panels and components.
Construction: Strengthening concrete and roofing materials.
Energy Sector: Reinforcing wind turbine blades and solar panels.
Consumer Goods: Producing items like surfboards and bicycles.
Consider the following factors:
Application Type: Determine whether it’s for structural reinforcement, insulation, or aesthetic purposes.
Strength Requirements: Assess the load-bearing needs of your project.
Environmental Conditions: Consider exposure to moisture, chemicals, or UV rays.
Budget: Balance performance requirements with cost constraints.
Applying fiberglass cloth involves:
Surface Preparation: Ensure the surface is clean, dry, and free from contaminants.
Cutting the Cloth: Trim the fiberglass cloth to the desired size.
Mixing Resin: Combine the resin and hardener according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Applying Resin: Brush or roll the resin onto the surface.
Laying the Cloth: Place the fiberglass cloth onto the resin-coated surface.
Saturating the Cloth: Apply more resin over the cloth to ensure full saturation.
Curing: Allow the resin to cure as per the recommended time and temperature.
Fiberglass Cloth: Woven fibers provide strength and flexibility, suitable for applications requiring a smooth finish.
Fiberglass Mat: Randomly oriented fibers offer uniform strength, ideal for applications needing bulk and thickness.
Fiberglass is made from natural materials and is recyclable. However, the production process can be energy-intensive. It’s important to consider the environmental impact of both manufacturing and disposal when using fiberglass products.