- +86-13775339109
- Jessica@nq-fiberglass.cn
- No 61 Fangxian, Danyang, Jiangsu
Table of Contents
ToggleWhen you’re comparing fiberglass and carbon fiber panels, it usually comes down to strength, weight, cost, and durability. Both materials are popular in industries like construction, automotive, aerospace, and marine, but they perform very differently.
This guide gives you a clear breakdown of what each material is, how they’re used, and when you should choose one over the other.
Fiberglass is a composite material made by combining fine glass fibers with a resin matrix. This combination creates a lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant material, making fiberglass an excellent option for a variety of applications.
Fiberglass is widely used for products that require a combination of strength, flexibility, and affordability. For example, fiberglass panels can be used in automotive parts, boat hulls, insulation, and construction materials.
There are several types of fiberglass, each with unique properties suited for specific industries:
Fiberglass is widely used in industries where affordability, flexibility, and corrosion resistance are needed, making it a go-to material for construction, automotive, marine, and consumer goods.
Carbon fiber is made from extremely thin strands of carbon atoms that are bonded together and then combined with a resin to form a strong yet lightweight material. Unlike fiberglass, carbon fiber is incredibly stiff, strong, and resistant to wear and tear under high stress.
Carbon fiber excels in applications where maximum strength and minimal weight are required, such as aerospace, luxury sports gear, and high-performance automotive parts.
Carbon fiber’s exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity make it ideal for high-performance industries, although it does come at a significantly higher cost due to its complex production process.

Feature | Fiberglass | Carbon Fiber |
Strength | Strong, flexible, impact-resistant | Stronger, stiffer, brittle under impact |
Weight | Lightweight (heavier than carbon) | 70% lighter than fiberglass |
Durability | Corrosion-resistant, flexible | Heat-resistant, but cracks under sudden stress |
Cost | Affordable, easy to source | Expensive, premium material |
Applications | Construction, boats, insulation, consumer goods | Aerospace, F1 racing, luxury sports gear |
Choose fiberglass if you need an affordable, durable, and flexible material for everyday applications, such as insulation, boat hulls, or automotive panels. Its versatility makes it ideal for applications that require a reliable and cost-effective solution without compromising on strength.

Choose carbon fiber if you require maximum strength and minimal weight, such as in aerospace components, luxury sports gear, or high-performance racing cars. Its superior performance justifies the higher cost in demanding, high-end applications.
For certain projects, a hybrid approach is the best solution. Combining carbon fiber with fiberglass creates a composite material that balances performance with cost-effectiveness. These hybrid composites are commonly used in industries such as automotive and sports equipment, where both strength and affordability are needed.
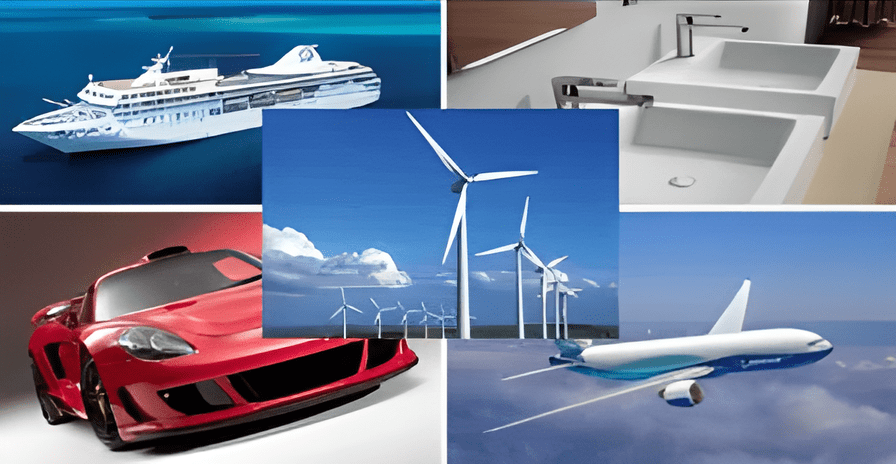
Let’s explore how these materials are applied in key industries:
Automotive: Fiberglass panels are often used for cost-effective and durable car bodies, while carbon fiber is used to reduce weight and enhance performance in high-end and racing vehicles.
Marine: Fiberglass hulls are resistant to saltwater, making them ideal for boats, while carbon fiber is used in high-performance vessels to enhance speed and fuel efficiency.
Aerospace: Fiberglass is commonly used for radomes and interior panels, while carbon fiber is critical for structural components, improving aircraft strength and fuel efficiency.
Construction: Fiberglass is used to reinforce concrete and as roofing material, while carbon fiber enhances the strength of bridges and large-scale infrastructure projects.
Consumer Goods: Fiberglass is found in products like ladders, bathtubs, and storage tanks, while carbon fiber is used in high-performance bicycles, tennis rackets, and surfboards.

Health Risks: Fiberglass particles can cause irritation. Always wear protective gear when handling fiberglass.
Environmental Impact: Both materials are energy-intensive to produce, and recycling options are still limited.
Disposal Challenges: Fiberglass is harder to recycle compared to metals.
Innovation in materials science is making both fiberglass and carbon fiber stronger, lighter, and more sustainable. New developments like nano-enhanced fiberglass, bio-based resins, and smart composites are reshaping the future of composites, making them even more efficient and environmentally friendly.
For example:
3D woven composites are being used to create stronger structures for aerospace and other demanding industries.
Bio-based resins are emerging as greener alternatives in the automotive and consumer goods industries.
So which should you choose?
Go with fiberglass if you want affordable, reliable, and versatile performance.
Choose carbon fiber if you need lightweight strength for high-end applications.
If you’re sourcing fiberglass fabrics, panels, or composites, we can provide customized solutions tailored to your project. Get in touch with us today for expert advice and competitive pricing.
Connect with an NQ expert to discuss your product needs and get started on your project.
Q1: What are the advantages of using fiberglass over other materials?
Fiberglass offers excellent strength, durability, and corrosion resistance at a lower cost compared to metals and other composites, making it ideal for a wide range of applications.
Q2: What is the difference between carbon fiber and fiberglass in terms of performance?
Carbon fiber is lighter, stronger, and more rigid than fiberglass, making it ideal for high-performance applications, while fiberglass is more affordable and offers good durability for less demanding projects.
Q3: Is carbon fiber stronger than steel?
Yes, carbon fiber has a higher strength-to-weight ratio than steel, making it both stronger and significantly lighter.
Q4: Is fiberglass considered plastic?
Fiberglass is a composite material — glass fibers embedded in resin. While it contains plastic resin, it is not pure plastic.
Q5: How much does carbon fiber cost compared to fiberglass?
Carbon fiber is significantly more expensive due to its complex production process, while fiberglass is more affordable and widely available.
Q6: What are the main applications of fiberglass?
Fiberglass is commonly used in construction, automotive panels, insulation, boat hulls, and consumer goods due to its cost-effectiveness and durability.
Q7: When should I choose carbon fiber instead of fiberglass?
Choose carbon fiber when your project requires maximum strength and minimal weight, such as aerospace parts, racing cars, or high-performance sporting goods.
Q8: Can fiberglass and carbon fiber be combined?
Yes, hybrid composites combine fiberglass and carbon fiber to balance performance with affordability.