- +86-13775339109
- Jessica@nq-fiberglass.cn
- No 61 Fangxian, Danyang, Jiangsu
Kevlar® and carbon fiber are both highly sought-after materials used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment. But what makes them unique? You may be wondering—what are the differences in their strength, durability, and ideal uses?
In this article, we’ll break down the key distinctions between Kevlar® and carbon fiber, providing you with a deeper understanding of how each material performs. Read on to discover which material best suits your needs!
Table of Contents
ToggleKevlar® is an incredibly strong synthetic fiber, categorized as an aramid fiber, which stands for aromatic polyamide. In simple terms, Kevlar®’s molecules consist of repeating chemical units that provide the material with outstanding tensile strength and heat resistance.
The production of Kevlar® begins with the synthesis of specific chemicals to form long molecular chains. These long chains are then spun into fibers, which are woven or braided into various products. This process results in a material that is both tough and flexible, capable of withstanding a range of external forces.
• Ultra-Strong and Lightweight
Kevlar® is five times stronger than steel by weight, yet it is incredibly light. This makes it perfect for applications that require high strength without adding unnecessary weight.
• Heat and Chemical Resistant
Kevlar® exhibits exceptional resistance to high temperatures and can withstand exposure to various chemicals, making it ideal for use in harsh environments.
• Flexible and Durable
Despite its formidable strength, Kevlar® maintains a high degree of flexibility, allowing it to absorb impacts and resist wear over time, ensuring durability in long-term use.
Body Armor, Helmets, Protective Gear
Kevlar® is most well-known for its use in protective gear, including bulletproof vests, helmets, and other safety equipment. Thanks to its superior strength and shock-absorbing qualities, it is the material of choice for personal protection.
Sporting Goods, Cables, Industrial Applications
Beyond protective gear, Kevlar® is also widely used in sporting goods like racing sails, bicycle tires, and tennis rackets. Additionally, it finds applications in industrial products such as high-strength ropes, cables, and automotive components.

What exactly is carbon fiber? It’s a super strong yet lightweight material made from carbon atoms arranged in a unique pattern. These atoms bond together to form long, thin fibers that are stronger than steel but way lighter.
How is it made? It starts with polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fibers, which are heated to crazy high temperatures (up to 3,000°C!). This heat removes everything but the carbon, leaving behind strong, pure carbon fibers. Then, these fibers are stretched to make them even stronger.
Once the fibers are made, they are spun into continuous filaments. These filaments are stretched and aligned so they can handle heavy loads without breaking. It’s like pulling taffy—only in this case, it makes the material stronger and more durable.
This process is important because even small changes can affect the quality of the carbon fiber. So, precision is key to getting top-notch, high-performance material.
Ever heard of prepreg carbon fiber? It’s carbon fiber soaked in resin. The filaments are combined with resin, then heated and pressed until the resin hardens. This process creates a super strong, rigid material that’s even more resistant to wear and tear.
Why does it matter? Because this combination makes carbon fiber even more durable, helping it stand up to things like moisture and UV damage.

Extremely High Strength-to-Weight Ratio:Want a material that’s stronger than steel but lighter? That’s carbon fiber. It’s perfect for things like airplanes and cars where reducing weight can make a big difference in performance. Lighter means more speed and better fuel efficiency—simple as that.
Stiffness and Durability:
Carbon fiber isn’t just strong—it’s stiff too. It doesn’t bend or warp easily, even under stress. Plus, it’s built to last, resisting wear and tear, fatigue, and even extreme temperatures. So, whether you’re flying at 30,000 feet or racing on a track, carbon fiber won’t let you down.
Aerospace:
Ever wonder why airplanes are so light but strong? It’s all thanks to carbon fiber. It’s used in aircraft wings, fuselages, and even landing gear to reduce weight and boost performance. Less weight means more fuel efficiency, which is a big deal in the skies.
Automotive Parts:
Carbon fiber is the secret weapon for high-performance cars. From car body panels to chassis, it helps reduce weight and increase fuel efficiency. Have you ever seen a sports car made almost entirely of carbon fiber? It’s the ultimate in performance.
Sports Equipment:
Think about the best bicycles, tennis rackets, or golf clubs—what do they all have in common? Carbon fiber! It makes equipment lighter, stronger, and more responsive. Ever tried hitting a tennis ball with a carbon fiber racket? You’ll feel the difference.
Construction:
Carbon fiber isn’t just for high-tech stuff—it’s also used to reinforce concrete and steel beams in construction. It’s lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant, which makes it perfect for tough jobs, like seismic retrofitting of buildings.

When it comes to choosing between Kevlar® and carbon fiber, it’s important to understand what sets them apart. Both materials are known for their strength and versatility, but they have distinct properties that make them better suited for different applications. Let’s break it down.
Kevlar®: Made from aramid fibers, it’s a synthetic polymer known for its strength and flexibility. It’s often used in protective gear because of its ability to absorb impacts.
Carbon Fiber: Made from carbon filaments, this material is rigid and incredibly strong, yet lightweight. It’s used in industries where structural strength and low weight are essential, like aerospace and automotive.
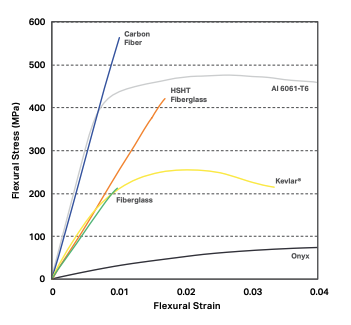
Kevlar®: Known for its ability to absorb impact and resist abrasion, Kevlar® is perfect for situations where flexibility and impact resistance are needed, such as in bulletproof vests.
Carbon Fiber: While carbon fiber is incredibly strong, it’s more suited for applications requiring rigidity. It’s also highly fatigue-resistant, meaning it doesn’t weaken after repeated stress.
Property | Kevlar® | Carbon Fiber |
Strength | Strong, flexible, energy-absorbing | Extremely strong, high tensile strength |
Weight | Slightly heavier (1.44 g/cm³) | Very lightweight (1.6-2.0 g/cm³) |
Key Benefit | Energy absorption | High stiffness and strength |
Both materials resist corrosion, but in different ways:
Which is more expensive, carbon fiber or Kevlar®?
Material | Uses | Benefits |
Kevlar® | Bulletproof vests, helmets, ropes, tires | Flexible, impact-resistant, energy absorption |
Carbon Fiber | Aircraft parts, car bodies, bicycles, sports gear | Lightweight, high stiffness, structural strength |
Kevlar® excels at flexible ballistic protection, while carbon fiber shines in creating high-performance, lightweight structural parts. Both materials are strong, but the choice depends on whether you need flexibility or rigidity.

Now that you have a clear understanding of Kevlar® and carbon fiber, it’s time to take the next step. Whether you’re looking for impact protection or lightweight strength, choosing the right material is essential for the success of your project.
If you’re ready to make the right choice for your needs, explore our range of Kevlar® and carbon fiber products. Whether you’re in aerospace, automotive, or sports equipment, we have the perfect solution for you.
Contact us now to discuss how we can help you find the best material for your next project!
Connect with an NQ expert to discuss your product needs and get started on your project.
Yes, absolutely! Carbon fiber is incredibly strong and can withstand heavy stress without breaking or deforming. It’s commonly used in industries where strength is critical, like aerospace and automotive.
Carbon fiber is highly durable. It’s fatigue-resistant, meaning it can handle repeated stress without weakening. It’s also resistant to wear and tear, making it last longer than many other materials.
In some ways, yes. Carbon fiber is stronger than steel in terms of its strength-to-weight ratio, meaning it’s stronger for the same weight. However, steel still has a higher tensile strength overall. It really depends on what you’re comparing—carbon fiber excels in lightweight, high-performance applications.
It depends on your needs. Carbon fiber excels in strength and rigidity, making it ideal for structural applications like aerospace and automotive parts. On the other hand, Kevlar® is renowned for its impact resistance and durability, making it the top choice for protective gear and applications where energy absorption is crucial.
So, carbon fiber offers superior strength and stiffness, while Kevlar® is better for flexibility and energy absorption.