- +86-13775339109
- Jessica@nq-fiberglass.cn
- No 61 Fangxian, Danyang, Jiangsu
Fiberglass is a strong, lightweight, and versatile material that has become essential across various industries. Made from fine glass fibers, it offers superior strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for everything from construction to aerospace.
In this guide, we’ll explore the different types of fiberglass and how they are produced. You’ll also learn about its key properties, like durability, insulation, and resistance to heat, which make it so popular.
Table of Contents
ToggleFiberglass is a composite material made from fine glass fibers combined with resin. This combination makes it lightweight yet incredibly strong, perfect for everything from construction to automotive applications.
The key components of fiberglass include:
Fiberglass is widely used in industries like construction, automotive, marine, and aerospace. Its lightweight nature, coupled with its resistance to heat, moisture, and impact, makes it an ideal material for various applications.
So, what’s in fiberglass? It’s mainly glass fibers, which give it strength, and resin that keeps everything together, creating a material that’s tough yet flexible.
Fiberglass was first developed in the 1930s. The idea of using glass fibers to reinforce materials emerged as engineers looked for stronger, lighter alternatives to metals. The first significant milestone came in 1932, when Owens Corning, a major manufacturer, patented a process for creating fiberglass insulation.
As the material evolved, it gained traction in various industries, especially after the 1940s, when fiberglass began to be used in boats, automobiles, and aerospace applications. By the 1950s, it became a popular choice for manufacturers due to its strength, light weight, and durability.
Fiberglass is made by pulling molten glass through fine holes to form fibers. These fibers are then combined with a resin, such as polyester or epoxy, to create a solid, durable material. The production process varies based on the type of fiberglass being created.
Different types of fiberglass are created based on the desired strength, flexibility, and application. You can dive deeper into the process in our detailed article on Fiberglass Material: What It Is and How It’s Made.

Fiberglass comes in various types and forms, each designed for specific applications. Below, we’ll cover some of the most commonly used types of fiberglass, along with its versatile forms.
A-glass, often referred to as “alkali-resistant glass,” is primarily used in applications where resistance to corrosion is important. It has a high silica content, which gives it good insulation properties. This type is commonly found in electrical insulation and chemical-resistant products, where durability is key.
C-glass is a type of glass known for its chemical resistance. It is made with a high boron content, making it highly resistant to corrosion from acids and alkalis. Due to this, C-glass is often used in environments where fiberglass is exposed to harsh chemicals, such as in the production of chemical tanks, pipes, and reinforcement in corrosive environments.
E-glass is the most common form of fiberglass and is widely used in general-purpose applications. It has good electrical properties, making it ideal for electrical insulation, as well as in composites for the automotive, marine, and construction industries. E-glass is known for its excellent tensile strength and versatility, often used in building materials and consumer products.
AE-glass, or alkali-earth glass, is a specialized form of fiberglass known for its improved chemical resistance, particularly to high temperatures and corrosive environments. This glass type combines the benefits of both E-glass and C-glass, providing higher mechanical strength and enhanced thermal resistance. It’s often used in industrial applications where high durability is required.S-glass
S-glass is a high-performance glass fiber that offers superior strength and stiffness compared to E-glass. With a higher tensile strength, S-glass is commonly used in aerospace, military, and high-end sporting equipment. Its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio makes it an ideal choice for products that require extreme durability without adding excessive weight, such as in aircraft parts and high-performance vehicles.Fiberglass Tape
Fiberglass tape is a woven fiberglass material that is coated with a resin to enhance its strength and heat resistance. It’s commonly used in electrical and thermal insulation, especially in applications that require a flexible, yet durable product. Fiberglass tape is often used for wrapping pipes, cables, and electrical components to protect against heat and mechanical stress.
Fiberglass Cloth
Fiberglass cloth is a fabric made from woven glass fibers and is used in a variety of applications, including automotive parts, boat hulls, and as reinforcement in composite materials. The fabric is lightweight yet strong, and its flexibility makes it ideal for applications that require molding and shaping. It’s also used in the manufacturing of insulation materials and as a base for certain coatings.
Fiberglass rope is made by twisting and braiding glass fibers together to form a strong, flexible cord. It is resistant to heat, chemicals, and abrasions, making it a great option for high-temperature environments like industrial furnaces and ovens. Fiberglass rope is commonly used for sealing, insulation, and packing in applications where durability and heat resistance are critical.
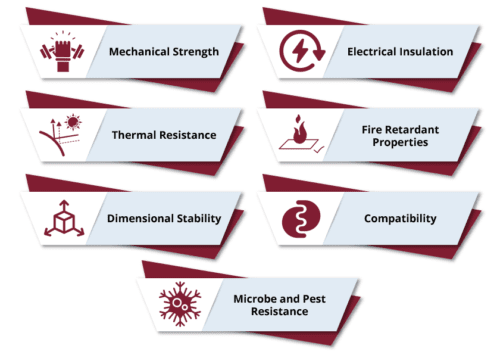
Fiberglass is renowned for its outstanding properties that make it an ideal material across a wide range of industries. Below, we explore its key characteristics that contribute to its versatility and performance.
Fiberglass boasts impressive tensile strength, meaning it can withstand significant stretching forces without breaking. This strength, combined with its resistance to damage from impact, makes it an ideal material for use in demanding environments. It doesn’t easily crack or bend under stress, offering long-term durability in both structural and composite applications.
Compared to materials like steel and aluminum, fiberglass is remarkably lightweight. This property makes it perfect for applications where weight reduction is crucial—such as in the aerospace and automotive industries. Despite its lightness, fiberglass retains flexibility, allowing it to be molded into various shapes while maintaining its strength. In contrast, steel and aluminum, though strong, can be heavy and less flexible.
Fiberglass performs exceptionally well in high-temperature environments, making it ideal for insulation and fireproofing applications. It remains stable and doesn’t degrade when exposed to heat, unlike many plastics or metals that can warp or melt. This heat resistance makes it popular in industries such as construction and electronics.
Fiberglass has a high mechanical strength-to-weight ratio, which means it can provide superior strength without the weight of traditional materials. Its resistance to fatigue and deformation over time adds to its reliability in products that endure repetitive stress, such as automotive parts and marine vessels.
Fiberglass is an excellent electrical insulator. Its dielectric properties make it an ideal choice for electrical and electronic applications. Whether used in circuit boards or insulation materials, fiberglass ensures reliable electrical performance without conductivity, safeguarding against electrical faults.
Fiberglass maintains dimensional stability across a wide range of temperatures and environmental conditions. Unlike metals that can expand or contract due to heat, fiberglass retains its shape and size, providing consistency and precision in various applications, from construction to aerospace.
Fiberglass is highly compatible with organic matrices like polyester and epoxy resins. This compatibility makes it ideal for creating composite materials, which combine the benefits of both the resin and the fiberglass for applications requiring extra strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear.
Unlike wood and certain metals, fiberglass doesn’t rot or degrade when exposed to moisture. This non-rotting property makes it a preferred material in marine environments, pipe linings, and construction, where exposure to water and humidity is common.
Fiberglass has low thermal conductivity, meaning it doesn’t transfer heat well. This property makes it ideal for applications requiring thermal insulation, such as insulation panels in buildings or as a component in appliance insulation. Fiberglass helps maintain consistent temperatures and prevents energy loss.
Fiberglass exhibits excellent dielectric permeability, which means it allows electrical fields to pass through it with minimal interference. This makes it ideal for high-frequency applications like communication cables and electronics, where low signal distortion is crucial.
Fiberglass is one of the most versatile materials available today, with applications spanning numerous industries due to its exceptional properties. Below, we dive into some of the major sectors where fiberglass is used extensively.
In construction, fiberglass plays a key role in insulation and roofing. Fiberglass insulation is widely used in homes and commercial buildings to help with thermal and sound insulation. Its lightweight and non-combustible properties make it ideal for energy-efficient buildings. Fiberglass is also used in concrete reinforcement, where its durability and corrosion resistance provide long-lasting structural support in bridges, highways, and other concrete infrastructures.
In the automotive industry, fiberglass is used for vehicle body parts, interior components, and reinforcements. It is commonly found in bumpers, hoods, and fenders, offering a lightweight alternative to metal without sacrificing strength. Fiberglass also improves fuel efficiency due to its lightness and is used in composite materials for electric vehicles and sports cars, making them both durable and energy-efficient.
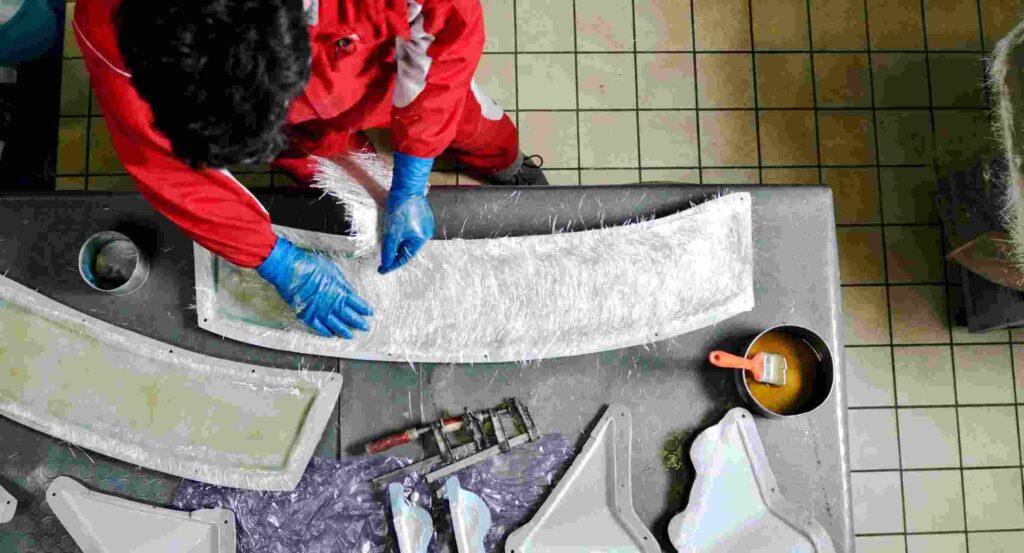

Fiberglass’s lightweight and strong properties make it invaluable in the aerospace and aviation industries. Aircraft components, such as fuselages, wing structures, and interior panels, benefit from fiberglass’s ability to reduce weight without compromising strength. Additionally, fiberglass helps improve fuel efficiency and performance, making it a key material in modern aviation.
Marine
Fiberglass is a dominant material in the marine industry, particularly in the production of boat hulls, yachts, and surfboards. Its corrosion resistance and waterproof qualities ensure that vessels can withstand harsh marine environments without deteriorating. Fiberglass boats are also lighter and more fuel-efficient, offering significant advantages over traditional materials like wood and metal.

In the consumer products sector, fiberglass is found in a variety of home appliances, sports equipment, and furniture. From dishwashers and dryers to swimming pool filters and snowboards, fiberglass enhances the durability and performance of many everyday items. Its lightweight nature and resistance to wear and tear make it a preferred choice for items that are exposed to frequent use or harsh conditions.
Fiberglass is used in the beverage industry for storage tanks, pipes, and filtration systems. Its resistance to chemicals and moisture makes it ideal for handling liquid products and maintaining the integrity of beverage storage systems.
In car washes, fiberglass is used for wash tunnel liners and equipment housing. Its resistance to water, chemicals, and wear makes it a great material for ensuring the longevity of equipment used in high-water and chemical environments.

Fiberglass is commonly used in the chemical industry for storage tanks, vessels, and pipes. Due to its corrosion resistance, fiberglass helps store and transport aggressive chemicals without degrading, making it essential for manufacturing plants dealing with corrosive materials.
In cooling towers, fiberglass is used for structural supports, piping, and basins. Its ability to resist moisture, chemicals, and high temperatures makes it an ideal material for environments where water cooling systems are needed.
Fiberglass is a go-to material for docks and marinas due to its resistance to water and weathering. It helps ensure the durability of floating structures, keeping them intact and functional even in harsh maritime conditions.

In food processing, fiberglass is used for conveyor belts, mixing tanks, and storage bins. Its resistance to heat, chemicals, and corrosion makes it ideal for environments that require strict hygiene standards and material durability.
Fiberglass is often used in the production of fountains and aquariums. Its ability to form complex shapes while being lightweight allows designers to create elaborate structures that are both durable and easy to maintain in outdoor or aquatic environments.
In manufacturing, fiberglass plays a critical role in molded parts, tooling, and reinforcement materials. Its versatility allows it to be shaped into many different forms, providing both strength and flexibility in production lines for a wide range of products.

Fiberglass is also used in the metals and mining industry for filtering systems, mineral processing equipment, and ventilation systems. Its resistance to high temperatures, corrosion, and abrasion makes it ideal for handling harsh environments and materials.
In power generation, fiberglass is used in turbine blades, cooling systems, and heat exchangers. Its thermal stability and strength make it a suitable material for high-performance applications where energy efficiency is key.
Fiberglass plays a key role in plating plants, where it is used for tanks and vessels to handle the corrosive nature of chemicals involved in electroplating processes. It ensures long-lasting performance and minimizes downtime due to equipment failure.
Pulp and Paper Industry
In the pulp and paper industry, fiberglass is used in filtering systems, storage tanks, and piping. Its resistance to chemicals and wear makes it an excellent choice for handling the aggressive conditions present in paper mills and similar facilities.
In addition to its use in vehicle body parts, fiberglass plays a major role in automotive applications such as interior panels, door linings, and exterior components for electric vehicles and sports cars. Its lightweight and strength enhance vehicle performance while reducing energy consumption.
In aerospace and defense, fiberglass is used in the manufacture of radomes, aircraft fuselages, and defense equipment. Its combination of strength, lightness, and resistance to environmental factors ensures optimal performance in the demanding environments of air and space.

Fiberglass continues to be a game-changing material across industries, thanks to its impressive strength, light weight, and resistance to heat, moisture, and chemicals. Whether you’re working in construction, automotive, or aerospace, there’s a fiberglass solution designed to meet your specific needs.
Now that you’ve explored the potential of fiberglass, consider how you can integrate it into your projects or product designs. If you’re ready to dive deeper into its applications or need guidance on selecting the right fiberglass type, explore our detailed guide on [Fiberglass Material: What It Is and How It’s Made].
Connect with an NQ expert to discuss your product needs and get started on your project.